How To Design The Ap Create Task Video
The last step shown under Algorithm, using repeat to clarify the structure is also a simple example of abstraction. It hides a lot of repetitive detail and shows the structure better. This type of abstraction is not what the AP Create Task is looking for though.
You used another abstraction as well. The way you actually wrote the algorithm in Unit 1 recognized that the 45° turn was \frac{1}{8} of the total turning of 360°. So you wrote the algorithm this way:
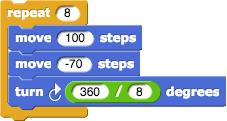
Changing both eights to fives in that algorithm would create a pinwheel with 5 branches. Instead of changing the numbers each time you wanted a new pinwheel, you created a block that contained the algorithm and let you just input whatever number of branches you want:
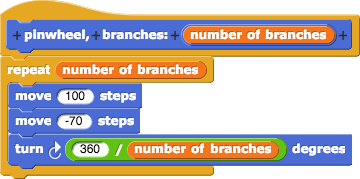
This is the kind of example you need to show for the Create Task: a custom block used multiple times in your project. Loops are an example of abstraction, but the expectation for the Create Task is that you create and submit your own example of abstraction rather than just pointing out existing abstractions like loop blocks.
The abstraction of pinwheel helps in three ways:
- It saves you from having to change two numbers each time you use the code, which is prone to error (such as accidentally changing only one of them but not the other).
- Instead of putting all this code

in your program everywhere you want it to draw a pinwheel, you now need only

- Your code is easier for someone else to read, because it now says what it does: it makes a pinwheel with 8 branches.
When you create a block and give it a name that describes its purpose, you are creating an abstraction. You are hiding the details and showing only the purpose. When you use that pinwheel block, it shows the structure of your program more clearly. Someone reading your program doesn't need to figure out what the details inside pinwheel do; they can tell from the name that it makes a pinwheel with a given number of branches.
Note that while packing your entire program into a single block might the page cleaner, it is not a good example of abstraction. The best examples of abstraction to highlight for the AP are pieces of code that you use multiple times in your program and are clearer because they are packed into a well-named block. You can often use what's in that block as an example of the algorithm for the purpose that the block serves.
How To Design The Ap Create Task Video
Source: https://bjc.edc.org/bjc-r/cur/performance-tasks/create-task/5-communicating.html?topic=nyc_bjc%2Fcreate-task.topic&course=bjc4nyc.html&novideo&noassignment
Posted by: valdeztherplis.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Design The Ap Create Task Video"
Post a Comment